Food Additives
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
- Food additives are substances added to foods to change the way they look or taste, how long they last, and how much nutrition they provide.
- Some people are sensitive to some additives and some may increase your risk for health problems.
- You can cut back on additives by reading food labels, eating less prepackaged food, and eating more fresh food.
________________________________________________________________________
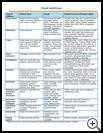
What are food additives?
Food additives are substances added to foods to:
- Help foods look and taste appealing. For example, adding colors or flavors to meats or fruit drinks.
- Improve the nutrition of food. For example, adding vitamins or minerals to bread, cereals, or milk.
- Preserve quality and freshness. For example, adding chemicals to prevent mold, bacteria, or to keep food from turning brown or spoiling.
- Improve the texture and keep foods from separating. For example, using chemicals to add smoothness, thickening, or the right level of moisture.
As a general rule, food additives do not include:
- Food ingredients such as salt and sugar
- Vitamins and minerals, unless they are added during processing
- Spices
Are food additives safe?
Congress directed the FDA to create a list of Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) chemicals in 1958. The list includes:
- Additives with a long history of safety
- Additives that qualified experts say are safe
- Additives shown to be safe for their intended use because they have been eaten by a large number of consumers
The FDA is not required to review and approve food additives classed as GRAS. Many additives have not been tested, but scientists consider them to be safe. Some additives that are found to be harmful may still be allowed, but only in very small amounts (1/100th of the amount that is known to be harmful). Research on the safety of food additives is ongoing. There are some concerns about food additives such as:
- MSG (used as a flavor enhancer). MSG may cause symptoms such as burning, tingling, or numbness in the neck, arms, and chest; headache, nausea, irregular heartbeat, and trouble breathing 20 minutes to 2 hours after eating foods that contain MSG.
- Sulfites such as potassium bisulfite, sodium bisulfite, sodium sulfite (used as preservatives). Sulfites cause allergic reactions in 5 out of 100 people with asthma.
- Sodium nitrites (used to add flavor and red color to meat). Studies have shown that people who eat a lot of processed meats have a higher risk of colorectal cancer. This may be due to nitrites that are added to lunch meats, hot dogs, bacon, and ham.
- Trans fat (used to make foods creamy or have longer shelf life). Listed as partially hydrogenated oils, trans fats have been shown to raise LDL (bad cholesterol), which increases your risk for heart disease. The FDA has given manufacturers until 2018 to remove partially hydrogenated oils from foods.
- Food dyes. Some people are sensitive or allergic to certain artificial colors, such as FD&C yellow#5 and #6. Some research shows that food dyes may make sensitive children hyperactive.
How can I cut back on additives in my diet?
- Read food labels. Food manufacturers are required to list all ingredients in the food on the label. The ingredients list includes any nutrients, color additives, preservatives, fats, or sugars that have been added. The ingredients used in the greatest amount are listed first. Some ingredients can be listed as flavors, spices, artificial flavoring, or artificial colors, without naming each one.
- Eat fresh foods instead of canned or packaged foods as much as possible. If you can’t get fresh foods, choose frozen fruits and vegetables without any additives.
- Avoid prepackaged meals and processed meats.
- Limit fast food, which usually contains a lot of preservatives, artificial flavorings, colorings and other additives.
Ask your healthcare provider for information about nutrition, diet, and health.