Ménière’s Disease
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
- Ménière’s disease is an inner ear problem that causes severe dizziness.
- Treatment includes medicine, hearing aids, eating a low salt diet, and sometimes surgery.
- If you are dizzy, you should lay down to avoid falling and do not get up until the dizziness passes.
________________________________________________________________________
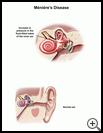
What is Ménière’s disease?
Ménière’s disease is a problem that affects the inner ear. It causes sudden spells of severe dizziness that can last from minutes to hours. The dizziness is usually described as a feeling of spinning (vertigo). There is often some loss of hearing as well. It usually affects just one ear, but it can happen in both ears.
Often Ménière’s disease is a mild illness and can be controlled with medicine. You may have symptoms that come and go throughout your life.
What is the cause?
The inner ear is made up of a system of fluid-filled tubes that help you keep your balance and help you hear. When fluid pressure in these tubes increases, you can feel very dizzy and have trouble hearing. The change in fluid can also lead to a temporary change in the chemicals in the fluid, which may also cause symptoms. What causes the fluid changes is not known, but possible triggers include injury, infection, and allergies.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms may include:
- A very severe sense of spinning that happens suddenly
- Noise (ringing, roaring, or buzzing) in your ear when the dizziness starts
- Loss of hearing in an ear that may get worse with an attack of dizziness
- A feeling of pressure or fullness in the ear
Symptoms may come and go. An attack typically lasts several hours. Attacks may come every few days, months, or years.
How is it diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms and medical history and examine you. Tests may include:
- Hearing tests
- A position test, in which you lie back and move your head in certain directions. If you have an inner ear problem, these movements will cause feelings of spinning and fast, jerky movements of your eyes. Your provider may have you wear magnifying goggles to help him see the eye movements. This test may be done with an ENG (electronystagmogram), which uses small wires pasted or taped to your head to measure and record eye movements
- A test with cold and warm water placed in your ear to see how your inner ear and nerves respond. The response is actually seen in small movements of your eyes. This test may also be done with an ENG.
- Balance and body position testing
You may be referred to an ear nose and throat specialist for tests or treatment. You may have tests or scans to check for other possible causes of your symptoms. These may include CT scan or an MRI, which uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to show detailed pictures of the brain.
How is it treated?
There is no cure for this disease, but treatments can help manage the symptoms. Usually the first step is to lower fluid pressure in your inner ear. Ways to do this include:
- Eating a low-salt diet. Some foods can cause or worsen ringing or other noises in your ear. For example, caffeine in coffee, tea and soft drinks or taking aspirin. Ask your provider if you should limit or avoid caffeine or other products.
- Wearing a hearing aid in the affected ear to help improve your hearing. You may be referred to an ear specialist for tests and to learn about options for hearing aids.
- Taking medicine to help your body get rid of salt and water, and help prevent nausea, vomiting, and dizziness.
- Using a device that keeps the inner ear from causing dizzy spells.
Some nonprescription medicines can worsen symptoms. Check with your provider or pharmacist before using these medicines.
Sometimes allergies can make symptoms worse. Your provider may recommend allergy testing and treatment with allergy medicines or allergy shots.
You may need surgery to stop the dizziness. For example:
- A drain may be put in the inner ear to help drain excess fluid.
- Medicine may be injected into your ear to stop the dizziness.
- The part of the inner ear that affects your sense of balance may be removed.
- The nerve in your ear that controls balance may be cut.
How can I take care of myself?
Follow the full course of treatment prescribed by your healthcare provider. In addition:
- If you are dizzy, you should lay down to avoid falling and not get up until the dizziness passes.
- If you smoke, try to quit. If someone else in your household smokes, ask them to smoke outside. Smoking can increase dizziness.
- If your dizziness does not allow you to continue your usual routine, rest at home. Avoid tasks that could endanger yourself or others if you suddenly get dizzy. This includes driving, using tools or machinery, or cooking.
- Take care of your health. Try to get at least 7 to 9 hours of sleep each night. If you want to drink alcohol, ask your healthcare provider how much is safe for you to drink. Learn ways to manage stress. Exercise according to your healthcare provider's instructions.
Ask your provider:
- How and when you will get your test results
- If there are activities you should avoid and when you can return to your normal activities
- How to take care of yourself at home
- What symptoms or problems you should watch for and what to do if you have them
Make sure you know when you should come back for a checkup. Keep all appointments for provider visits or tests.