Prostate Problems
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
- The prostate gland is part of a man's reproductive system and is located between the bladder and the penis. You may have prostate problems such as swelling, inflammation, or cancer.
- Treatment depends on the cause of the problem and may include medicine for infection, surgery, hormone therapy, or radiation therapy.
- Have regular medical checkups, including rectal exams. See your healthcare provider right away if you have symptoms of a prostate problem.
________________________________________________________________________
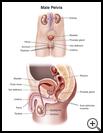
What is the prostate?
The prostate gland is part of a man's reproductive system. It is about the size of a walnut and located between the bladder and the penis. The prostate gland surrounds the upper part of the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out through the penis. It makes fluid that nourishes sperm and helps carry it out of the body during sex.
Prostate problems are common in men over the age of 50.
What are common prostate problems and what causes them?
Three common prostate problems are:
- Prostatitis
Prostatitis is swelling and irritation (inflammation) of the prostate. Sometimes it is caused by infection with bacteria or a virus. The bacteria can spread to the prostate through the urethra after sex. The bacteria can also spread to the prostate through the bloodstream. The prostate can also get inflamed without infection. Often the cause is not known.
Prostatitis may cause a burning pain when you urinate or when you release semen during sex. You may feel the urge to urinate more often than usual. You may have pain in your lower back or groin.
- Enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia, or BPH)
The prostate starts to get bigger at puberty, but it usually does not get big enough to cause problems until around the age of 50. When the prostate is enlarged, it can put pressure on the urethra, irritate the bladder, and cause problems with urination. You may feel more sudden and stronger urges to urinate. You may urinate more often, especially at night. You may have trouble starting and stopping the flow of urine, and you may have a weak stream of urine.
BPH is a common health problem for men over age 60.
- Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in American men. The cause is not known.
Prostate cancer often has no symptoms, especially in the early stages. The symptoms can be very similar to symptoms of prostatitis and BPH. For example, symptoms may include problems with urination, such as trouble starting or stopping the flow of urine; pain or burning when you urinate; and a frequent and urgent need to urinate, especially at night.
How are they diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, your medical history, and your family history, and examine you. Tests may include:
- Blood tests
- Rectal exam, which your provider does by gently putting a lubricated and gloved finger in your rectum. Your provider may also place his or her other hand on your belly to feel and check the size and shape of your organs.
- Biopsy of the prostate. A biopsy is the removal of a small sample of tissue for testing. Your healthcare provider may use an ultrasound, which uses sound waves to show pictures of the prostate, to help with the biopsy.
How are they treated?
When prostatitis is caused by an infection, it may be treated with antibiotics.
If you have an enlarged prostate but your symptoms are mild, you may not need treatment other than 1 or more exams a year. Sometimes symptoms get better without treatment. Treatments may include:
- Medicine
- Procedures to destroy excess prostate tissue
- Surgery to remove excess prostate tissue
Prostate cancer often grows very slowly. It may be treated with surgery, radiation therapy, or hormone therapy. If you are over 75 years old and have other medical problems, it may not be treated at all as long as your prostate is not causing urinary problems.
How can I take care of myself?
- Have regular medical checkups, including rectal exams.
- Talk with your healthcare provider about the PSA test if you are over 50 or have a strong family history of prostate cancer.
- See your provider if you have symptoms of a prostate problem.