Kidney Cancer (Renal Cell Carcinoma)
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
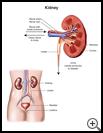
- The kidneys are inside your belly, on either side of your spine just above your waist. They make urine and help control blood pressure. Kidney cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the kidney.
- You may have surgery to remove part or all of a kidney, renal artery embolization to stop blood flow to the tumor, radiation therapy, or biological therapy.
- Ask your healthcare provider how to take care of yourself at home.
________________________________________________________________________
What is kidney cancer?
Kidney cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the kidney. This growth of cancer cells is called a tumor. Renal cell cancer (or renal cell carcinoma) is the most common type of kidney cancer.
The kidneys are inside your belly, on either side of your spine just above your waist. They make urine by taking waste products and extra salt and water from the blood. They also help control blood pressure.
The sooner cancer is found and treated, the better your chances for recovery. However, even advanced cancer can usually be treated. Treatment may slow or stop the growth of the cancer and ease symptoms for a time. Ask your healthcare provider what you can expect with the type of cancer that you have.
What is the cause?
The exact cause of kidney cancer is not known. Chemicals that can cause kidney cancer can get into your blood from working with chemicals such as asbestos, weed killers, and others. Your kidneys filter out most of the chemicals, but some stay in your urine. Tumors can start after your kidneys have been exposed for many years to these chemicals.
Smokers are much more likely to get kidney cancer. If you smoke cigarettes and you are also exposed to chemicals that cause kidney cancer, your risk increases even more.
Your risk for getting kidney cancer is higher if you:
- Are over 40 years old
- Are male
- Are very overweight (obese)
- Have Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome (a rare hereditary disease)
- Are on long-term kidney dialysis
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms may include:
- Blood in the urine, which is the most common sign
- A lump that can be felt in the belly or side
- Pain in the lower back or side that does not go away
- Loss of appetite
- Unexpected weight loss
- Feeling tired all the time
- Fever and night sweats
Many of these symptoms can also be caused by urinary infections or other problems.
What is metastasis?
The spread of cancer cells from one part of the body to other parts is called metastasis. What causes cancer to spread is not known. Cancer cells can:
- Grow into the area around the tumor
- Travel to other parts of the body through the bloodstream or the lymph system. The lymph system is part of your body's system for fighting infection. The lymph system consists of lymph nodes that store blood cells (lymphocytes) to fight infection and vessels that carry fluid, nutrients, and wastes between your body and your bloodstream.
New tumors then grow in these other areas. When kidney cancer spreads, it most often affects the lungs, liver, and brain. What causes cancer to spread to other parts of the body is not known. Sometimes your first symptoms of cancer are in the part of the body where the cancer has spread. The symptoms of kidney cancer that has spread to another part of your body depend on where the tumors are. For example:
- If the cancer has spread to the lungs, you may have a cough or trouble breathing.
- If the cancer has spread to the brain, you may have trouble talking or walking.
- If the cancer has spread to the liver, you may have yellowish skin, pain, or swelling in your belly.
How is it diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms and medical history and examine you. You may have tests such as:
- Blood tests
- Ultrasound, which uses sound waves to show pictures of the kidneys
- CT scan, which uses X-rays and a computer to show detailed pictures of the kidneys
- MRI, which uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to show detailed pictures of the kidneys
- Arteriogram, which is a special X-ray of the arteries and veins of the kidneys
Sometimes kidney tumors are found when X-rays or scans are done for other reasons.
You may need more lab tests and scans to check if the cancer has spread to other parts of your body.
How is it treated?
Some things to think about when making treatment decisions are:
- Your age
- Your overall health
- The stage of the cancer (how advanced the cancer is)
- Whether the cancer has spread to other parts of your body
The usual treatment is surgery to remove all or part of the kidney that has cancer. Most people can live with just 1 kidney. If both kidneys need to be removed, you will need dialysis or a kidney transplant. Dialysis uses a machine to clean your blood when your kidneys don’t work well or have been removed.
Other possible treatments are:
- Renal artery embolization, which is a procedure done to block blood flow to the tumor so that it will shrink
- Radiation therapy, which uses high-energy X-rays to kill cancer cells
- Biological therapy, which uses medicine to help your immune system fight the cancer or targeted medicines that block the growth of the kidney cancer cells
Your treatment will also include:
- Preventing infections
- Controlling pain or other symptoms you may have
- Controlling the side effects from treatments
- Helping you manage your life with cancer
Often, more than 1 treatment is used. After treatment, you will need to have regular follow-up visits with your healthcare provider.
Ask your healthcare provider about clinical trials that might be available to you. Clinical trials are research studies to find effective cancer treatments. It’s always your choice whether you take part in one or not.
How can I take care of myself?
If you have been diagnosed with renal cell cancer:
- Talk about your cancer and treatment options with your healthcare provider. Make sure you understand your choices.
- Follow the full course of treatment prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Ask your healthcare provider:
- How and when you will get your test results
- How long it will take to recover
- If there are activities you should avoid and when you can return to your normal activities
- How to take care of yourself at home
- What symptoms or problems you should watch for and what to do if you have them
Make sure you know when you should come back for a checkup.
Other things that may help include:
- Eat a healthy diet and get regular exercise as recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Get plenty of rest.
- Try to reduce stress and take time for activities that you enjoy. It may help to talk with a counselor about your illness.
- Talk with your family and your healthcare providers about your concerns. Ask your healthcare provider any questions you have about the disease, treatments, side effects of the treatments, sexual activity, support groups, and anything else that concerns you.
- If you smoke, try to quit.
- Ask your provider if you need to avoid drinking alcohol. It may interfere with medicines you are taking. Alcohol can also make it harder for white blood cells to fight infections.
- Tell your provider if your treatment causes discomfort. Usually there are ways to help you feel more comfortable.
For more information, contact:
- American Cancer Society, Inc.
800-227-2345
http://www.cancer.org - National Cancer Institute
800-422-6237 (TTY: 800-332-8615)
https://www.cancer.gov/