Sinus Surgery
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
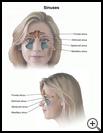
- The sinuses are hollow spaces in the bones of your face and front of your skull. Mucus drains through the small openings from the sinuses to the nose. You may need surgery to create an extra or enlarged pathway to help your sinuses drain more easily.
- Balloon sinuplasty uses a thin, flexible tube to gently move the bones in the nose and open blocked pathways. FESS uses a flexible, lighted tube to look at the inside of the nose and up into the sinuses to enlarge the pathways.
- Ask your healthcare provider how long it will take to recover and how to take care of yourself at home.
________________________________________________________________________
What is sinus surgery?
Sinus surgery is done to open blocked sinuses. The sinuses are hollow spaces in the bones of your face and front of your skull. They connect with the nose through small openings. Like the nose, they are lined with tissue (membranes) that make mucus. Mucus drains through the small openings from the sinuses to the nose.
You may need surgery to create an extra or enlarged pathway to help your sinuses drain more easily. Also, medicines that get absorbed through the mucous membranes of the nose and sinuses work better if the pathways are bigger.
When is it used?
Sinus surgery may be done to treat:
- Sinusitis, which is swelling and irritation of the linings of the sinuses. The pathways from the sinuses to the nose are very narrow. When drainage of mucus from the sinuses is blocked, the sinuses get swollen and irritated. They may also get infected with bacteria, a virus, or fungus. Allergies or irritation from pollen, mold, dust, or smoke can also cause swelling of the sinuses. Sometimes a tooth infection spreads to the sinuses.
If sinusitis is a problem for you after treatment by your regular healthcare provider, you may go to an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist. The ENT specialist will check for an infection, a growth, or a deformed bone that may be blocking your sinuses.
- Nasal polyp, which is a small growth (polyp) in the lining of your nose or sinuses that blocks the pathway
- Septal deviation, which means that the cartilage in your nose is crooked. Nose (nasal) cartilage is the smooth, flexible wall inside your nose between your nostrils.
How do I prepare for this procedure?
- Make plans for your care and recovery after you have the procedure. Find someone to give you a ride home after the procedure. Allow for time to rest and try to find other people to help with your day-to-day tasks while you recover.
- You may or may not need to take your regular medicines the day of the procedure. Tell your healthcare provider about all medicines and supplements that you take. Some products may increase your risk of side effects. Ask your healthcare provider if you need to avoid taking any medicine or supplements before the procedure.
- Tell your healthcare provider if you have any food, medicine, or other allergies such as latex.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you when to stop eating and drinking before the procedure. This helps to keep you from vomiting during the procedure.
- Follow your provider's instructions about not smoking before and after the procedure. Smokers may have more breathing problems during the procedure and heal more slowly. It’s best to quit 6 to 8 weeks before surgery.
- Follow any other instructions your healthcare provider gives you.
- Ask any questions you have before the procedure. You should understand what your healthcare provider is going to do. You have the right to make decisions about your healthcare and to give permission for any tests or procedures.
What happens during the procedure?
The procedure may be done in your healthcare provider’s office or in a surgery center or hospital.
You will be given local or general anesthesia to keep you from feeling pain during the procedure. Local anesthesia numbs your nose. The medicine is usually given as a shot into the area. If the nose or mouth needs to be numbed, it may be done using nose drops or a spray.
General anesthesia relaxes your muscles and puts you into a deep sleep.
Types of sinus surgery include:
- Balloon sinuplasty uses a thin, flexible tube (catheter) placed in the nose. The tube has a balloon that gently stretches to move the bones in the nose and open blocked pathways. Usually, you will have less pain and bleeding if the balloon is used.
- Functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) uses a flexible, lighted tube to look at the inside of the nose and up into the sinuses to enlarge the pathways. CT imaging may be used to help your healthcare provider view the inside of the sinuses during the procedure.
Your healthcare provider will know what areas of your sinuses need surgery based on your symptoms and the tests done before surgery. Your provider will choose the surgery that will work best to treat your sinus problem.
What happens after the procedure?
You will be in the recovery area after surgery until you are ready to go home. Most people go home the same day.
Ask your healthcare provider:
- How long it will take to recover
- If there are activities you should avoid and when you can return to your normal activities
- How to take care of yourself at home
- What symptoms or problems you should watch for and what to do if you have them
Make sure you know when you should come back for a checkup. Keep all appointments for provider visits or tests.
What are the risks of this procedure?
Every procedure or treatment has risks. Some possible risks of this procedure include:
- You may have problems with anesthesia.
- You may have infection, bleeding, or blood clots.
- Other parts of your body may be injured during the procedure.
Ask your healthcare provider how these risks apply to you. Be sure to discuss any other questions or concerns that you may have.