Testicular Exploration
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
- Testicular exploration is a surgery to examine the testicles.
- This procedure may be done to check for problems such as infection, twisting, or cancer. It may also be done to bring down an undescended testicle, or remove one or both testicles.
- Ask your provider how long it will take to recover and how to take care of yourself at home.
- Make sure you know what symptoms or problems you should watch for and what to do if you have them.
________________________________________________________________________
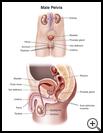
What is a testicular exploration?
A testicular exploration is a procedure done to examine the testicles. The testicles are part of the male reproductive system. They make sperm and the male hormone, testosterone. They are in a sac of loose skin, called the scrotum or scrotal sac. The scrotum is below the penis.
When is it used?
The procedure may be done to:
- Check for cancer of the testicles
- Remove a sample of tissue (biopsy) to help find the cause of infertility (being unable to conceive a child)
- Check for twisting or infection of the testicles
- Bring an undescended testicle down to the scrotum if it is high in the groin or abdomen
- In some cases, remove one or both testicles
Ask your healthcare provider to explain why you are having the procedure and any risks.
How do I prepare for this procedure?
- Make plans for your care and recovery after you have the procedure. Find someone to give you a ride home after the procedure. Allow for time to rest and try to find other people to help with your day-to-day tasks while you recover.
- Follow your healthcare provider's instructions about not smoking before and after the procedure. Smokers may have more breathing problems during the procedure and heal more slowly. It is best to quit 6 to 8 weeks before surgery.
- You may or may not need to take your regular medicines the day of the procedure. Tell your healthcare provider about all medicines and supplements that you take. Some products may increase your risk of side effects. Ask your healthcare provider if you need to avoid taking any medicine or supplements before the procedure.
- Tell your healthcare provider if you have any food, medicine, or other allergies such as latex.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you when to stop eating and drinking before the procedure. This helps to keep you from vomiting during the procedure.
- Follow any other instructions your healthcare provider gives you.
- Ask any questions you have before the procedure. You should understand what your healthcare provider is going to do. You have the right to make decisions about your healthcare and to give permission for any tests or procedures.
What happens during the procedure?
You will be given a regional or general anesthetic to keep you from feeling pain. A regional anesthetic numbs the part of your body where you will have the surgery while you stay awake. You may also be given medicine to help you relax. The medicine can make you drowsy or you may fall asleep before the procedure. General anesthesia relaxes your muscles and puts you into a deep sleep.
Your healthcare provider will make a cut either in your groin or scrotum so he or she can examine the testicle. Your testicle may need to be removed if:
- Your provider suspects cancer in the testicle.
- You have a severe infection that cannot be treated in other ways.
- The testicle is badly damaged.
What happens after the procedure?
You may go home later that day or stay in the hospital overnight, depending on your condition. Ask your healthcare provider:
- How long it will take to recover
- If there are activities you should avoid and when you can return to your normal activities
- How to take care of yourself at home
- What symptoms or problems you should watch for and what to do if you have them
Make sure you know when you should come back for a checkup. Keep all appointments for provider visits or tests.
What are the risks of this procedure?
Every procedure or treatment has risks. Some possible risks of this procedure include:
- You may have problems with anesthesia.
- The testicle may be damaged, leaving you infertile (unable to conceive a child), if the other testicle also does not work.
- You may have infection or bleeding.
Ask your healthcare provider how these risks apply to you. Be sure to discuss any other questions or concerns that you may have.