Ringing in the Ears (Tinnitus)
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
- Tinnitus is a ringing in one or both your ears.
- Treatment depends on the cause, and may include removing earwax, medicine, or surgery.
- Sometimes hearing aids or retraining therapy can help you get used to or mask the ringing.
- Background noise from fans or sound machines can help you not hear the ringing as much.
________________________________________________________________________
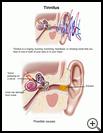
What is tinnitus?
Tinnitus is a noise that you hear in one or both of your ears or in your head. It is a symptom, not a disease. Those who have it describe it as a ringing, buzzing, humming, heartbeat, or chirping noise.
What is the cause?
Sound waves go into the outer ear, down the ear canal, and to the eardrum in the middle ear. The sound waves make the eardrum and small bones behind the eardrum vibrate. The vibrating bones make the fluid in the inner ear vibrate. This bends tiny hair cells in the inner ear. The hair cells turn the movement into electrical signals that get sent through nerves to your brain. These nerves control hearing and balance.
Tinnitus may be caused by:
- Earwax buildup
- Being exposed to very loud noises (like an explosion) or loud noises over time (like machinery or loud music)
- Fluid in the middle ear
- Damage or disease in the inner ear
- A tumor or damage to nerves that send signals to the brain
- A problem in the hearing centers of your brain
- Infection
- Diseases of the heart or blood vessels
- Some medicines
How is it diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms and medical history and examine you. You will have hearing tests.
You may be referred to an ear nose and throat specialist for tests or treatment. You may have tests or scans to check for other possible causes of your symptoms. These may include CT scan or an MRI, which uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to show detailed pictures of the brain.
How is it treated?
Treatment depends on the cause, and may include:
- Earwax removal
- Medicine to lessen or stop the tinnitus
- Surgery to remove a tumor or drain fluid
- Hearing aids, if you also have a hearing loss
- Masking devices, such as fans or sound machines that play ocean or rain sounds, to block the sounds of the tinnitus
- Tinnitus retraining therapy (TRT). TRT plays low-level noise to help you get used to unwanted sound. TRT also usually includes counseling.
If medicines cause tinnitus, your provider may be able to prescribe a different medicine.
Tinnitus may get better over time even without treatment, or it may be a life-long problem.
How can I take care of myself?
Follow the full course of treatment prescribed by your healthcare provider. In addition:
- Ask your provider if you should limit or avoid caffeine or other products. Some foods and nonprescription medicines can cause or worsen ringing or other noises in your ear. For example, caffeine in coffee, tea, and soft drinks, or taking aspirin.
- Take care of your health. Try to get at least 7 to 9 hours of sleep each night. If you want to drink alcohol, ask your healthcare provider how much is safe for you to drink. Learn ways to manage stress. Exercise according to your healthcare provider's instructions.
Ask your provider:
- How and when you will get your test results
- How long it will take to recover
- If there are activities you should avoid and when you can return to your normal activities
- How to take care of yourself at home
- What symptoms or problems you should watch for and what to do if you have them
Make sure you know when you should come back for a checkup. Keep all appointments for provider visits or tests.
How can I help prevent tinnitus?
One of the most common causes of tinnitus is exposure to too much or too loud noise. Use foam ear plugs or ear muffs to protect your hearing when you are around loud noise. Keep the volume down when listening to music.