Brimonidine Tartrate, Ophthalmic
bri-MOH-ni-deen TAR-trate
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
- This medicine is used in the eyes to treat or prevent high pressure in the eyes. Use it exactly as directed.
- This medicine may cause unwanted side effects. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effects that are serious, continue, or get worse.
- Tell all healthcare providers who treat you about all the prescription medicines, nonprescription medicines, supplements, natural remedies, and vitamins that you take.
________________________________________________________________________
What are other names for this medicine?
Type of medicine: alpha2 agonist
Generic and brand names: brimonidine tartrate, ophthalmic; Alphagan P
What is this medicine used for?
This medicine (in the form of eyedrops) is used to treat high pressure in the eyes. High pressure in the eyes may be caused by glaucoma or other conditions.
This medicine may be used to treat other conditions as determined by your healthcare provider.
What should my healthcare provider know before I take this medicine?
Before taking this medicine, tell your healthcare provider if you have ever had:
- An allergic reaction to any medicine
- A stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- Depression
- Heart disease or a recent heart attack
- High blood pressure
- Kidney or liver disease
- Low blood pressure
- Raynaud's disease or Buerger’s disease
Do not take an MAO inhibitor and this medicine within 14 days of each other.
Females of childbearing age: Tell your healthcare provider if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Do not breast-feed while taking this medicine without your healthcare provider's approval.
How do I use it?
Check the label on the medicine for directions about your specific dose. Use this medicine exactly as your healthcare provider prescribes. Do not use more of it or use it more often than prescribed.
Do not use this medicine in children under age 2.
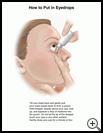
Wash your hands before putting medicine in your eyes. Tilt your head back and gently pull your lower eyelid down to form a pouch. Hold the dropper directly above your eye, look up, and squeeze a drop of the medicine into the pouch. Close your eyes for a minute or two and with a fingertip press gently on the inside corner of your eye to keep the medicine from draining out. Do not rub your eyes.
To avoid contaminating the medicine, do not let the tip of the dropper touch your eye or any other surface. After use, put the cap on tightly. Do not rinse the dropper. Do not use the medicine if it changes color or looks cloudy.
If you use other eyedrops, wait at least 5 minutes after putting this medicine in your eyes before you use the other medicine.
What if I miss a dose?
If you miss a dose, use it as soon as you remember unless it is almost time for the next scheduled dose. In that case, skip the missed dose and use the next one as directed. Do not use double doses. If you are not sure of what to do if you miss a dose, or if you miss more than one dose, contact your healthcare provider.
What if I overdose?
An acute overdose of this medicine is not likely to cause life-threatening symptoms. If you think that you or anyone else may have taken too much of this medicine, call the poison control center at 800-222-1222.
What should I watch out for?
Your healthcare provider will want to see you regularly to be sure your condition is under control.
If you wear soft contact lenses, wait at least 15 minutes after putting the medicine in your eyes before putting in your lenses.
This medicine can cause fatigue or drowsiness and can affect your vision. Do not drive or operate machinery until you are fully alert and can see clearly.
If you need emergency care, surgery, lab tests, or dental work, tell the healthcare provider or dentist you are using this medicine.
What are the possible side effects?
Along with its needed effects, your medicine may cause some unwanted side effects. Some side effects may be very serious. Some side effects may go away as your body adjusts to the medicine. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effects that continue or get worse.
Life-threatening (Report these to your healthcare provider right away. If you cannot reach your healthcare provider right away, get emergency medical care or call 911 for help.): Allergic reaction (hives; itching; rash; trouble breathing; tightness in your chest; swelling of your lips, tongue, and throat).
Serious (Report these to your healthcare provider right away.): Extreme eye irritation or redness, bleeding in the eye, dizziness, swelling of the feet or legs, slow or irregular heartbeat.
Other: Eye irritation, watery eyes, dry mouth, feeling that something is in the eye, headache, fatigue, drowsiness, blurred vision, eye pain, eye dryness, bitter or sour taste, nasal dryness, stuffy or runny nose, nausea, constipation, sensitivity to light, trouble sleeping.
What products might interact with this medicine?
When you take this medicine with other medicines, it can change the way this or any of the other medicines work. Nonprescription medicines, vitamins, natural remedies, and certain foods may also interact. Using these products together might cause harmful side effects. Talk to your healthcare provider if you are taking:
- ACE inhibitors such as benazepril (Lotensin), captopril, enalapril (Vasotec), fosinopril, lisinopril (Prinivil, Zestril), quinapril (Accupril), and ramipril (Altace)
- Alpha blockers such as doxazosin (Cardura), prazosin (Minipress), and terazosin
- Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) such as azilsartan (Edarbi), candesartan (Atacand), eprosartan (Teveten), irbesartan (Avapro), losartan (Cozaar), olmesartan (Benicar), telmisartan (Micardis), and valsartan (Diovan)
- Antianxiety medicines such as alprazolam (Xanax), clorazepate (Gen-Xene, Tranxene), diazepam (Valium), lorazepam (Ativan), and oxazepam
- Antidepressants such as amitriptyline, desipramine (Norpramin), imipramine (Tofranil), and nortriptyline (Pamelor)
- Antihistamines such as chlorpheniramine (Chlor-Trimeton), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), hydroxyzine (Vistaril), and meclizine (Dramamine)
- Antipsychotic medicines such as chlorpromazine, clozapine (Clozaril, FazaClo), fluphenazine, haloperidol (Haldol), olanzapine (Zyprexa), perphenazine, thioridazine, and trifluoperazine
- Antiseizure medicines such as carbamazepine (Carbatrol, Epitol, Equetro, Tegretol), felbamate (Felbatol), gabapentin (Neurontin), lamotrigine (Lamictal), phenytoin (Dilantin, Phenytek), topiramate (Qudexy, Topamax, Trokendi), and valproic acid (Depacon, Depakene, Depakote)
- Barbiturates such as butabarbital (Butisol), pentobarbital (Nembutal), phenobarbital, and secobarbital (Seconal)
- Beta blockers (for the eyes) such as betaxolol, carteolol (Ocupress), levobunolol (AKBeta, Betagan), metipranolol (OptiPranolol), timolol (Betimol, Timoptic, Timoptic XE), and timolol/dorzolamide (Cosopt)
- Beta blockers (taken by mouth) such as acebutolol (Sectral), atenolol (Tenormin), bisoprolol (Zebeta), carteolol, carvedilol (Coreg), labetalol (Trandate), metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol), nadolol (Corgard), nebivolol (Bystolic), sotalol (Betapace, Sorine), and timolol
- Calcium channel blockers such as amlodipine (Norvasc), amlodipine/atorvastatin (Caduet), diltiazem (Cardizem, Cartia, Tiazac), felodipine, isradipine (DynaCirc), nicardipine (Cardene), nifedipine (Adalat CC, Procardia), and verapamil (Calan, Covera, Verelan)
- Clonidine (Catapres, Kapvay)
- Digoxin (Lanoxin)
- Diuretics (water pills) such as amiloride, bumetanide, chlorothiazide (Diuril), furosemide (Lasix), hydrochlorothiazide (Microzide), spironolactone (Aldactone), torsemide (Demadex), and triamterene (Dyrenium)
- Doxepin (Silenor)
- MAO inhibitors such as isocarboxazid (Marplan), phenelzine (Nardil), selegiline (Eldepryl, Emsam, Zelapar), and tranylcypromine (Parnate) (Do not take this medicine and an MAO inhibitor within 14 days of each other.)
- Muscle relaxants such as baclofen (Gablofen, Lioresal), carisoprodol (Soma), cyclobenzaprine (Amrix), dantrolene (Dantrium), methocarbamol (Robaxin), and tizanidine (Zanaflex)
- Narcotic pain medicines such as codeine, fentanyl (Abstral, Actiq, Duragesic, Fentora, Sublimaze), hydromorphone (Dilaudid, Exalgo), meperidine (Demerol), methadone (Dolophine, Methadose), morphine (Kadian, MS Contin), and oxycodone (OxyContin, Roxicodone)
- Natural remedies such as bayberry, black cohosh, California poppy, ephedra, ginger, ginseng, goldenseal, gotu kola, hawthorn, licorice, shepherd’s purse, St. John's wort, and valerian
- Nausea medicines such as prochlorperazine (Compro) and promethazine
- Other products in your eyes
- Propranolol (Hemangeol, Inderal, InnoPran)
- Sleeping pills such as eszopiclone (Lunesta), flurazepam, temazepam (Restoril), triazolam (Halcion), zaleplon (Sonata), and zolpidem (Ambien, Edluar, Intermezzo)
Do not drink alcohol while you are taking this medicine without your healthcare provider's approval.
Do not use other products in your eyes while you are using this medicine without your healthcare provider's approval.
If you are not sure if your medicines might interact, ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider. Keep a list of all your medicines with you. List all the prescription medicines, nonprescription medicines, supplements, natural remedies, and vitamins that you take. Be sure that you tell all healthcare providers who treat you about all the products you are taking.
How should I store this medicine?
Store this medicine at room temperature. Keep the container tightly closed. Protect it from heat, high humidity, and bright light.
This advisory includes selected information only and may not include all side effects of this medicine or interactions with other medicines. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for more information or if you have any questions.
Ask your pharmacist for the best way to dispose of outdated medicine or medicine you have not used. Do not throw medicine in the trash.
Keep all medicines out of the reach of children.
Do not share medicines with other people.
Last modified: 2016-09-22
Last reviewed: 2015-07-31