Etonogestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol, Vaginal Ring
et-oh-noh-JES-trel ETH-in-il es-tra-DY-ole
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
- This medicine is a soft ring that you insert into your vagina to prevent pregnancy. Use it exactly as directed.
- This medicine may cause unwanted side effects. Smoking while you are using this medicine increases the risk of serious side effects such as heart attack, stroke, and blood clots. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effects that are serious, continue, or get worse.
- Tell all healthcare providers who treat you about all the prescription medicines, nonprescription medicines, supplements, natural remedies, and vitamins that you take.
________________________________________________________________________
What are other names for this medicine?
Type of medicine: contraceptive (birth control)
Generic and brand names: etonogestrel/ethinyl estradiol, vaginal ring; NuvaRing
What is this medicine used for?
This medicine is a soft ring that you insert into your vagina to prevent pregnancy. The ring is a monthly form of birth control. The ring contains a combination of a progestin and estrogen, the same two female hormones in birth control pills. After the ring is inserted, it releases hormones into your body.
This medicine may be used to treat other conditions as determined by your healthcare provider.
What should my healthcare provider know before I take this medicine?
Tell your healthcare provider if you have ever had:
- An allergic reaction to any hormones or medicines
- A stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- Blood clots in your legs, lungs, or eyes
- Breast lumps or an abnormal mammogram
- Cancer of the breast, uterus, cervix, or vagina
- Depression
- Diabetes
- Disease of the heart valves or any other heart disease
- Headaches along with symptoms such as vomiting, double vision, unsteadiness, weakness, or personality changes
- Heart disease or a heart attack
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol or high triglycerides
- Liver, gallbladder, or kidney disease
- Prolapse of the uterus, bladder, or rectum
- Seizures
- Severe constipation
- Thyroid problems
- Toxic shock syndrome
- Unexplained vaginal bleeding or irregular menstrual periods
- Yellowing of the eyes or skin (jaundice) during pregnancy or during past use of hormonal birth control
Tell your healthcare provider if you have recently had or are scheduled to have a long period of bed rest after major surgery or a broken bone in a cast. Also, tell your healthcare provider if you have recently had a baby, miscarriage, or abortion.
Tell your healthcare provider if you smoke. Smoking while you are using this medicine increases the risk of serious side effects such as heart attack, stroke, and blood clots. Women who are over the age of 35 and smoke should not use this medicine.
Females of childbearing age: Do not take this medicine during pregnancy because it may harm the baby. Tell your healthcare provider if think you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant while taking this medicine. Do not breast-feed while taking this medicine without your healthcare provider's approval.
How do I use it?
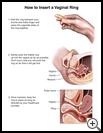
Read and follow the patient instructions that come with the ring. If you do not understand how to use the ring, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist to explain.
If you are switching from another form of hormonal birth control, such as pills, implants, injections, or a progesterone-that contain IUD, talk with your healthcare provider about how to start using the ring.
Check with your healthcare provider before using this medicine in girls who have not yet reached puberty.
What if I miss a dose?
Leave the ring in place continuously for 3 weeks. If the ring comes out during the 3 weeks, rinse it off with lukewarm water and put it back in within 3 hours. If ring is out of your vagina for more than 3 hours, contact your healthcare provider.
What if I overdose?
If you or anyone else has intentionally taken too much of this medicine, call 911 or go to the emergency room right away. If you pass out, have seizures, weakness or confusion, or have trouble breathing, call 911. If you think that you or anyone else may have taken too much of this medicine, call the poison control center. Do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning. The poison control center number is 800-222-1222.
Symptoms of an acute overdose may include: nausea, vomiting, vaginal bleeding.
What should I watch out for?
Smoking while you use this medicine increases your risk of side effects. The risk increases with age and the number of cigarettes smoked a day. Talk to your healthcare provider about ways to quit smoking.
If you have light bleeding while using the ring, do not stop using the ring. The problem will usually go away. If it doesn’t go away, check with your healthcare provider.
You need to see your healthcare provider at least once a year for checkups while using this medicine. Do not use this medicine for longer than 1 year without a complete physical exam.
This medicine only prevents pregnancy. It does not prevent sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) such as HIV or herpes.
Some medicines may make the ring less effective. You may need to use another method of birth control if you take these medicines. Tell all healthcare providers who treat you that you are using the ring.
While using the ring, do not use a diaphragm when you need a back-up method of birth control.
If you wear contact lenses and notice a change in your vision or it becomes difficult to wear your lenses, contact your healthcare provider.
If you need emergency care, surgery, lab tests, or dental work, tell the healthcare provider or dentist you are using birth control hormones. You may need to stop taking hormones at least 4 weeks before the surgery or a long period of bedrest. You may have a greater risk of blood clots. Birth control hormones may change some blood test results.
If you have diabetes: This medicine may affect your blood sugar level and change the amount of insulin or other diabetes medicines you may need. Talk to your healthcare provider about this.
What are the possible side effects?
Along with its needed effects, your medicine may cause some unwanted side effects. Some side effects may be very serious. Some side effects may go away as your body adjusts to the medicine. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effects that continue or get worse.
Life-threatening (Report these to your healthcare provider right away. If you cannot reach your healthcare provider right away, get emergency medical care or call 911 for help.):
- Allergic reaction (hives, itching, rash, tightness in your chest, trouble breathing)
- Sharp chest pain or pressure, coughing blood, or sudden shortness of breath
- Pain in the calf or any leg pain that does not go away
- Sudden weakness, numbness, or tingling, especially on one side of your body; sudden or severe headache; sudden trouble with vision, speech, balance, or walking
Serious (Report these to your healthcare provider right away.):
- Yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes (jaundice), especially with fever, tiredness, loss of appetite, dark urine, or light-colored bowel movements
- Sudden high fever, vomiting, diarrhea, sunburn-like rash, muscle aches, dizziness, or fainting
- Severe pain, swelling, or tenderness in the abdomen
- Breast lumps or tenderness
- Irregular vaginal bleeding or spotting that happens in more than 1 menstrual cycle or lasts for more than a few days
- Swelling of your hands or ankles
- Trouble sleeping, weakness, lack of energy, or depression
- Trouble urinating
Other: Vaginal or urinary infection, vaginal discharge or itching, vaginal tissue irritation or pain, headache, darkening of the skin on the face, weight gain, nausea, vomiting, acne, decreased sexual desire.
What products might interact with this medicine?
When you take this medicine with other medicines, it can change the way this or any of the other medicines work. Nonprescription medicines, vitamins, natural remedies, and certain foods may also interact. Using these products together might cause harmful side effects. Talk to your healthcare provider if you are taking:
- Acetaminophen and medicines that contain acetaminophen
- Acitretin (Soriatane)
- Antianxiety medicines such as alprazolam (Xanax), clonazepam (Klonopin), clorazepate (Gen-Xene, Tranxene), diazepam (Valium), lorazepam (Ativan), oxazepam, and temazepam (Restoril)
- Antibiotics such as amoxicillin (Amoxil, Moxatag), ampicillin, demeclocycline, dicloxacillin, doxycycline (Doryx, Monodox, Vibramycin), erythromycin (E.E.S., Ery-Tab, Erythrocin), minocycline (Dynacin, Minocin, Solodyn), nafcillin, oxacillin, penicillin VK, rifabutin (Mycobutin), rifampin (Rifadin), rifapentine (Priftin), and tetracycline
- Antidepressants such as amitriptyline, duloxetine (Cymbalta), fluvoxamine (Luvox), and nortriptyline (Pamelor)
- Antifungal medicines such as clotrimazole, fluconazole (Diflucan), griseofulvin (Grifulvin V, Gris-PEG), itraconazole (Sporanox), ketoconazole (Nizoral), miconazole (Monistat, Oravig), posaconazole (Noxafil), and voriconazole (Vfend)
- Antipsychotic medicines such as asenapine (Saphris), clozapine (Clozaril, FazaClo), and pimozide (Orap)
- Antiseizure medicines such as carbamazepine (Carbatrol, Epitol, Equetro, Tegretol), ethotoin (Peganone), felbamate (Felbatol), fosphenytoin (Cerebyx), gabapentin (Neurontin), lamotrigine (Lamictal), levetiracetam (Keppra), oxcarbazepine (Trileptal), phenytoin (Dilantin, Phenytek), primidone (Mysoline), rufinamide (Banzel), tiagabine (Gabitril), topiramate (Qudexy, Topamax, Trokendi), and valproic acid (Depacon, Depakene, Depakote)
- Aprepitant (Emend)
- Artemether/lumefantrine (Coartem)
- Barbiturates such as butabarbital (Butisol), pentobarbital (Nembutal), phenobarbital, and secobarbital (Seconal)
- Bosentan (Tracleer)
- Cancer medicines such as anastrozole (Arimidex), enzalutamide (Xtandi), exemestane (Aromasin), mitotane (Lysodren), and tretinoin (Atralin, Renova, Retin-A)
- Cholesterol-lowering medicines such as atorvastatin (Lipitor), cholestyramine (Prevalite), colesevelam (Welchol), colestipol (Colestid), lomitapide (Juxtapid), and rosuvastatin (Crestor)
- Corticosteroids such as betamethasone, cortisone, dexamethasone, fludrocortisone, hydrocortisone (A-Hydrocort, Cortef), methylprednisolone (Medrol, Solu-Medrol), prednisolone (Omnipred, Orapred, Prelone), prednisone (Prednisone Intensol), and triamcinolone (Aristospan, Kenalog)
- Doxepin (Silenor)
- HIV medicines such as atazanavir (Reyataz), darunavir (Prezista), delavirdine (Rescriptor), elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/tenofovir (Stribild), etravirine (Intelence), fosamprenavir (Lexiva), indinavir (Crixivan), lopinavir/ritonavir (Kaletra), nelfinavir (Viracept), nevirapine (Viramune), ritonavir (Norvir), and saquinavir (Invirase)
- Immunosuppressants such as cyclosporine (Gengraf, Neoral, Sandimmune) and mycophenolate (CellCept, Myfortic)
- Isotretinoin (Absorica, Amnesteem, Claravis, Myorisan, Zenatane)
- Lumacaftor/ivacaftor (Orkambi)
- Medicines to treat or prevent blood clots such as apixaban (Eliquis), dabigatran (Pradaxa), dalteparin (Fragmin), enoxaparin (Lovenox), heparin, rivaroxaban (Xarelto), and warfarin (Coumadin)
- Mifepristone (Korlym, Mifeprex)
- Morphine (Kadian, MS Contin)
- Natural remedies such as black cohosh, chasteberry, dong quai, evening primrose oil, ginseng, red clover, soy, St. John's wort, topical progesterone, and wild yam
- Ospemifene (Osphena)
- Stimulants such as armodafinil (Nuvigil) and modafinil (Provigil)
- Theophylline
- Thyroid medicines such as levothyroxine (Levo-T, Levothroid, Levoxyl, Synthroid, Unithroid), liothyronine (Cytomel, Triostat), liotrix (Thyrolar), and thyroid USP (Armour Thyroid, Nature-Throid)
- Tizanidine (Zanaflex)
- Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) in large doses
Do not use other vaginal products while using this medicine without your healthcare provider's approval.
Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you need to avoid products that contain grapefruit, Seville oranges, or tangelos while you are taking this medicine. These fruits and juices can affect the way this medicine works and may increase your risk of serious side effects.
If you are not sure if your medicines might interact, ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider. Keep a list of all your medicines with you. List all the prescription medicines, nonprescription medicines, supplements, natural remedies, and vitamins that you take. Be sure that you tell all healthcare providers who treat you about all the products you are taking.
How should I store this medicine?
Store this medicine at room temperature for no more than 4 months. Keep the container tightly closed. Protect it from heat, high humidity, and bright light. Do NOT use past the expiration date.
This advisory includes selected information only and may not include all side effects of this medicine or interactions with other medicines. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for more information or if you have any questions.
Ask your pharmacist for the best way to dispose of outdated medicine or medicine you have not used. Do not throw medicine in the trash.
Keep all medicines out of the reach of children.
Do not share medicines with other people.
Last modified: 2016-10-11
Last reviewed: 2016-05-26