Carotid Artery Disease
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
- Carotid artery disease is a disease caused by a narrowing or blockage of the carotid arteries. If blood flow to your brain is slowed, it can cause temporary symptoms, stroke, or death.
- You may need treatment with medicines or surgery.
- Follow your healthcare provider’s advice about exercising, eating a healthy diet, watching your weight, not smoking, and checking your blood pressure.
________________________________________________________________________
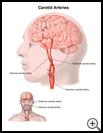
What is carotid artery disease?
Carotid artery disease is a disease caused by a narrowing or blockage of the carotid arteries. These 2 arteries in your neck bring blood to your head and brain. A narrowing or blockage of a carotid artery can slow or stop blood flow. If blood flow to your brain is slowed, it can cause temporary symptoms such as dizziness, partial blindness, or numbness. It can also cause stroke or death.
What is the cause?
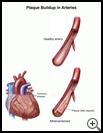
Most often narrowing of the arteries is caused by fatty deposits called plaque that build up in blood vessels and make them narrower. The narrowing decreases the amount of blood flow to your brain. Pieces of plaque may break off from the wall of a blood vessel and form clots that can block blood flow to the brain.
Your risk of developing fatty deposits is higher if you:
- Have a family history of carotid artery disease
- Smoke
- Have high blood pressure
- Have diabetes or insulin resistance
- Are very overweight
- Don’t get enough exercise
- Have high levels of blood fat--for example, high cholesterol
What are the symptoms?
Most people with carotid artery disease have no symptoms. The most common symptoms of carotid artery disease are transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) or stroke. A TIA is a brief loss in brain function. It happens when the brain does not get enough blood because a blood vessel is blocked for a short time. Symptoms of TIA and stroke are the same, except TIA symptoms go away within 24 hours and stroke symptoms may not. A TIA is different from a stroke because it does not cause any lasting damage to the brain. Even if your symptoms are gone within 24 hours, it's possible that there is brain damage and you have had a stroke.
It helps to think of the word FAST (face, arm, speech, time) to remember TIA or stroke symptoms and what to do. The symptoms come on FAST and may include:
- Face/Head
- Weakness, numbness, drooping, or tingling of face (may just be on one side)
- Trouble seeing (one or both eyes)
- Severe headache
- Trouble thinking
- Trouble swallowing
- Feeling dizzy along with one or more of the symptoms listed above
- Arm/Leg
- Weakness, numbness, or tingling in your arm or leg (may be on just one side of your body)
- Trouble walking or moving your arm or leg
- Speech
- Trouble talking or understanding speech
- Time
- Call 911 for emergency help right away if you have symptoms of a TIA or stroke.
If you have had a TIA, you have a high risk of having a stroke. Do not ignore symptoms of a TIA. Get emergency medical care to help prevent a stroke and to be tested to see if your symptoms were caused by blockage of your carotid arteries.
How is it diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms and medical history and examine you. Tests may include:
- MRI, which uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to show detailed pictures of your brain and blood vessels
- CT scan, which uses X-rays and a computer to show detailed pictures of your brain and blood vessels
- Ultrasound, which uses sound waves to show pictures of the blood vessels in your neck and brain
- Angiogram, which uses dye injected into a vein and X-rays to look at blood flow in the carotid arteries or brain
How is it treated?
The goal of treatment is to prevent more blockages of the arteries and stroke.
Your healthcare provider may prescribe medicine that helps prevent blood clots or medicine to lower cholesterol. Your provider may tell you to take a low-dose aspirin every day. Aspirin lowers the chance that blood clots will form and lowers your risk of having a stroke caused by a blood clot. However, some strokes are caused by bleeding and aspirin may increase your risk of having this type of stroke. If you are having sudden symptoms of a stroke, do not take aspirin unless recommended by your healthcare provider.
If your carotid artery is severely blocked and is causing symptoms, you will likely need a procedure to open the blood vessel.
- Carotid endarterectomy involves making cuts in your neck and the artery and then removing the blockage.
- Carotid angioplasty and stenting involves passing a balloon-tipped tube (catheter) into the blocked artery in your neck. Once the catheter is in the proper place, the balloon is inflated to open the blood vessel and improve blood flow. A metal mesh device called a stent is usually left in the artery to help keep the blood vessel open.
How can I take care of myself?
Follow the full course of treatment prescribed by your healthcare provider. Take any medicines exactly as prescribed.
Try to have a healthy lifestyle:
- Eat a healthy diet.
- Try to keep a healthy weight. If you are overweight, lose weight.
- Stay fit with the right kind of exercise for you.
- If you smoke, try to quit. Talk to your healthcare provider about ways to quit smoking.
Get your cholesterol levels and blood pressure checked by your healthcare provider regularly.
If you have high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, or another medical problem, follow your treatment plan.
Ask your healthcare provider:
- How and when you will get your test results
- How long it will take to recover
- If there are activities you should avoid and when you can return to your normal activities
- How to take care of yourself at home
- What symptoms or problems you should watch for and what to do if you have them
Make sure you know when you should come back for a checkup. Keep all appointments for provider visits or tests.
How can I help prevent carotid artery disease?
Talk to your healthcare provider about your personal and family medical history and your lifestyle habits. This will help you know what you can do to lower your risk for carotid artery disease. Taking good care of your health, including a healthy lifestyle, can help prevent this disease.
Taking a low-dose aspirin every day may help prevent a heart attack or stroke. Not everyone should take aspirin. Ask your healthcare provider if you should take aspirin and if so, how much to take.