Breast Cancer in Women: Early Detection
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
- Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in women in the US. It is also a leading cause of death from cancer. With regular checks of the breast, most cancers can be found at an early stage.
- To find cancer early, have regular medical checkups by your healthcare provider and have mammograms according to your provider's recommendations.
______________________________________________________________________
Why is it important to find breast cancer early?
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer in women in the US. It is also a leading cause of death from cancer. With regular checks of the breast, most cancers can be found at an early stage, before they spread to other parts of the body. When breast cancer is found early it can often be cured.
Any woman can get breast cancer. If you have risk factors, it doesn’t mean that you’ll get breast cancer. Most women have some risk factors but don’t get breast cancer. You may have a higher risk of breast cancer if:
- You are over 60 years old
- You have had breast cancer before or you have had some noncancerous breast diseases
- You have a family history of breast or ovarian cancer, especially a mother, sister, or daughter, but also other relatives on either your father’s or mother’s side
- You have inherited a change in genes called BRCA1 and BRCA2. This change increases your risk for breast cancer
- You have had radiation therapy to the chest
- You drink alcohol (the more you drink, the higher your risk)
- You are overweight after going through menopause
- You don’t get a lot of regular exercise
- You started menstruating before age 12 and/or went through menopause after age 55
- You never gave birth to a child or you had your first child after age 30
- You did not breastfeed
- You have taken hormone therapy with estrogen and progesterone after menopause
What are the best ways to find breast cancer early?
You can:
- Have regular medical checkups that include a check of your breasts by your healthcare provider.
- Have regular mammograms according to your provider's recommendations.
If you are at high risk for breast cancer, you may also need to be screened with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
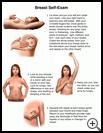
Breast self-exam
Ask your healthcare provider if you need to do breast self-exams. Self-exams can help you know what your breasts look and feel like, which helps you notice changes that need to be checked by your healthcare provider.
You can do a breast self-exam at any time. It helps if you do your self-exam on the same date every month. If you are still having periods, the best time to do the exam is a few days after your period.
If you notice any of the following changes in your breast, see your provider right away:
- You have a lump that is new or feels unusual, whether it is tender or not
- Your nipple is painful or starts turning into the breast
- You have new wrinkling or dimpling of the skin
- The nipple and surrounding skin is red or has a scaly rash
- You have a discharge of fluid from the nipple (other than breast milk if you are breast-feeding)
Exams by your healthcare provider
Have a breast exam by your healthcare provider at least every 3 years if you are 20 to 39 years old and every year after the age of 40. Your provider may be able to find lumps that you are not able to find when you do a self-exam. In addition, a trained examiner can find lumps in areas that are hard for a mammogram to find, such as deep under the breast, near the chest wall.
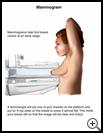
Mammograms
A mammogram is a special X-ray of the breast. It can show abnormal areas that are too small to feel, so it is a good way to screen for early breast cancer. Mammograms find most breast cancers, but they do not find all cancers. Breast self-exams and physical exams by your provider may find cancers not found with a mammogram. The exams may also find cancers that develop between mammograms.
Medical organizations do not agree on how often you should have a mammogram.
The US Preventive Services Task Force (2009) recommends a mammogram every 2 years for women 50 to 74 years old.
The American Cancer Society recommends that women with an average risk of breast cancer should have a screening mammography every year from ages 45-54 years. Women ages 55 years and older should have screening every 2 years, or they can continue yearly. Women should be able to begin yearly screening between the ages of 40 and 44 years (2015). Talk to your healthcare provider about when you should start having mammograms and how often you should have them.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
MRI is another way to screen for breast cancer. It may be done even if you have a mammogram, since neither method alone can find all breast cancers.
You may need an MRI if your risk for breast cancer is very high because:
- You have inherited a change in genes called BRCA1 and BRCA2. This change increases your risk for breast cancer
- You have had radiation therapy to the chest
- You have had breast cancer before or you have had a noncancerous breast disease
- You have a family history of breast or ovarian cancer (especially mother, sister, or daughter, but also other relatives on either your father’s or mother’s side)
You may also need an MRI for screening if you have thick breast tissue, which can affect the accuracy of mammogram results.
If you are not sure if these risks apply to you, ask your healthcare provider if you need a breast MRI.
You may worry if you are told that your mammogram is not normal or that there are changes since your last mammogram. You may need more tests or scans to find out if there is a problem. Very often, it turns out to be a normal change in your breast tissue, or a problem that is not cancer. Talk with your healthcare provider about the best choice for you.