Diabetes: Eye Problems
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
- High blood glucose can damage your eyes. Eye problems caused by diabetes are the leading cause of blindness in Americans over the age of 20.
- Follow your diabetes treatment plan so that you have fewer problems, and see your eye care provider every year, even if you do not have problems with your vision.
________________________________________________________________________
How are eye problems related to diabetes?
Eye problems can be a long-term complication of diabetes. High blood glucose can damage your eyes. If you have both diabetes and high blood pressure, you are at higher risk of developing eye problems. Eye problems caused by diabetes are the leading cause of blindness in Americans over the age of 20.
What are the most common eye problems?
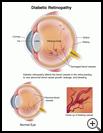
- Diabetic retinopathy: This is a problem with the blood vessels in your retina. The retina is the lining at the back of your eye that senses light coming into the eye. The retina has tiny blood vessels that can be damaged by long-term high blood glucose and high blood pressure. Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of permanent blindness from diabetes.
- Glaucoma: Glaucoma is an eye disease that damages the nerve that carries visual messages to the brain (optic nerve). This is usually caused by high pressure inside your eye. Damage to your optic nerve can cause a permanent loss of vision. Glaucoma needs to be diagnosed and treated early to prevent blindness. People with diabetes are much more likely to have glaucoma. Having regular eye exams is very important to test for glaucoma because your eyes may be damaged before you notice changes in vision.
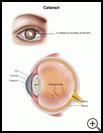
- Cataracts: A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of your eye. The lens is located inside your eye behind the colored part of your eye. For some people, the lens gets cloudier over time and causes vision problems. Cataracts are more common and happen at an earlier age in people who have diabetes.
- Blurry vision: When your blood glucose is out of control and often goes from high levels to low levels and back, the shape of the lens of your eye changes and vision gets blurry. Good control of blood glucose can prevent this.
- Diabetic keratopathy: High blood glucose weakens the cornea, which is the clear outer layer on the front of your eye. This causes tiny breaks or sores that are usually painful. However, diabetes also damages the nerves in the cornea, which means that sores can get very bad, or even infected, without causing pain.
How can I help prevent eye problems?
Follow your diabetes treatment plan so that you have fewer problems. A healthy lifestyle may help. For example:
- Eat a healthy diet and keep a healthy weight.
- Stay fit with the right kind of exercise for you.
- Control your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels.
- If you smoke, try to quit. Talk to your healthcare provider about ways to quit smoking.
- If you want to drink alcohol, ask your healthcare provider how much is safe for you to drink.
If you have diabetes, see your eye care provider every year, even if you do not have problems with your vision. Let your eye care provider know that you have diabetes and what medicines you take. If you have eye changes due to diabetes, your eye care provider may want you to have exams more often.