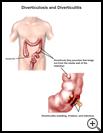
Diverticulosis
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
- Diverticula are tiny pouches or weak areas that bulge out from the inside wall of the intestine, usually in the colon. When you have diverticula in your intestines, it is called diverticulosis.
- If you have diverticulosis with no symptoms, your healthcare provider may recommend that you add more fiber to your diet.
- Ask your healthcare provider what symptoms or problems you should watch for and what to do if you have them.
________________________________________________________________________
What is diverticulosis?
Diverticula are tiny pouches or weak areas that bulge out from the inside wall of the intestine. The pouches are usually in the part of the intestine called the colon. They look like small thumbs poking out of the side of the intestine. When you have diverticula in your intestines, it is called diverticulosis.
What is the cause?
The exact cause of diverticulosis is not known. It is possible that too little fiber in the diet may cause hard stools or constipation. Your muscles strain to move stool that is too hard. The high pressure causes the weak spots in your colon to bulge out and form pouches. If stool or bacteria get caught in these pouches, it can cause swelling, irritation, and infection. This is called diverticulitis.
You may be at risk for diverticulosis if you are overweight, you smoke, or you take medicines like aspirin or steroids. It is more common in older adults, but can happen before age 50, especially in men.
What are the symptoms?
Usually diverticulosis does not cause any symptoms. It may be found when you have tests done for other reasons. If you do have symptoms, they may include:
- Pain in the lower left part of your belly. You may feel the pain most of the time, or it may come and go.
- A change in bowel habits, either constipation or diarrhea
Diverticulosis can also cause painless bleeding from the rectum.
How is it diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms and medical history and examine you. Tests may include:
- Colonoscopy, which uses a flexible, lighted tube put through your rectum to look at the inside of your colon. A similar test called a sigmoidoscopy looks at just the lower one-third of your colon. This test may also be done after a special dye is put into your rectum to show the walls of your intestine.
- Barium enema, which is an X-ray taken of the belly after barium is inserted through the rectum to show the walls of the intestine and any possible problems. Barium is a liquid that helps your intestines show up well on the X-ray.
- Blood tests
How is it treated?
If you have diverticulosis, with no symptoms, your healthcare provider may recommend you add more fiber to your diet. You can do this by eating more whole-grain products, such as whole-wheat and bran products (breads, cereals, and muffins). Also eat more fruits and raw or cooked vegetables. Ask your healthcare provider if you should take fiber supplements.
There is no proof that any foods cause diverticulosis, but you may want to avoid eating foods that can irritate the diverticula, such as popcorn kernels, sunflower seeds, sesame seeds, and nuts. If these foods do not seem to cause you pain or other symptoms, you may eat them.
How can I take care of myself?
Follow the full course of treatment prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Ask your provider:
- How and when you will get your test results
- How long it will take to recover
- If there are activities you should avoid and when you can return to your normal activities
- How to take care of yourself at home
- What symptoms or problems you should watch for and what to do if you have them
Make sure you know when you should come back for a checkup. Keep all appointments for provider visits or tests.
How can I help prevent diverticulosis?
The best way to try to prevent diverticulosis is to do the things that help you have bowel movements that are soft and easy to pass. For example:
- Eat a healthy diet with lots of fiber.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Get enough regular exercise.