Ectopic Pregnancy
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
- An ectopic pregnancy happens when a baby starts growing outside the uterus. Most often it happens in one of the fallopian tubes that lead from the ovaries to the uterus and is called a tubal pregnancy.
- If an ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed within the first 6 weeks of pregnancy, the pregnancy can be ended with medicine. Otherwise, you will need surgery to remove the pregnancy.
- Follow the full course of treatment prescribed by your healthcare provider. Ask how long it will take to recover and when you can return to your normal activities.
________________________________________________________________________
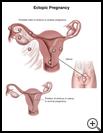
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy happens when a baby starts growing outside the uterus. The uterus is the muscular organ at the top of the vagina. Most often it happens in one of the fallopian tubes that lead from the ovaries to the uterus and is called a tubal pregnancy. Rarely, an ectopic pregnancy can happen in the ovary, cervix, or somewhere else in the abdomen.
Ectopic pregnancies are usually diagnosed within the first 2 months of pregnancy, sometimes before you know you are pregnant. An ectopic pregnancy can cause serious or life-threatening problems. It must be treated as soon as possible.
What is the cause?
An ectopic pregnancy may happen when something stops or slows a fertilized egg from passing through the fallopian tube and into the uterus. Things that may cause this are:
- Scarring from infection or from surgery on the tubes, ovaries, or appendix
- A defect in the fallopian tube that you have had since you were born
- Endometriosis, which is a growth of tissue from the lining of the uterus outside the uterus
- A previous ectopic pregnancy
You also have a greater risk of ectopic pregnancy if:
- Your mother was exposed to DES (a medicine sometimes given to pregnant women before 1970).
- You smoke.
- You have had problems getting pregnant or have had infertility treatments.
- You have an IUD in place when you get pregnant.
- Had surgery to open your fallopian tubes (after having them tied to prevent pregnancy).
- You are older than 35.
Sometimes the cause is not known.
What are the symptoms?
The symptoms may be mild or they may be severe and dangerous. Early symptoms can be the same as the symptoms of early pregnancy or other less serious conditions. These symptoms may include:
- Missed period or abnormal bleeding
- Pain in your lower belly or pelvis or low back
- Breast tenderness or morning sickness
The ectopic pregnancy can rupture (burst), damage your pelvic organs, and cause severe internal bleeding. A tubal pregnancy may rupture while you are having a bowel movement, especially if you are straining. The symptoms of a rupture may include:
- Sudden severe pain in the lower belly
- Pale skin, fast heart rate, and dizziness
- Fainting from low blood pressure caused by bleeding
- Shoulder pain
How is it diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms and medical history and examine you. Tests may include:
- A pregnancy test
- An ultrasound, which uses sound waves to show pictures of your abdomen, tubes, ovaries, and uterus
- Culdocentesis, which uses a needle passed through the vagina to look for blood or other fluids in the space behind the vagina
- Laparoscopy, which uses a small lighted tube put into the belly through a small cut to look at the organs and tissues inside the belly
How is it treated?
If an ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed within the first 6 weeks of pregnancy, the pregnancy can be ended with medicine. Otherwise, you will need surgery to remove the pregnancy. You will be given a general anesthetic to keep you from feeling pain. General anesthesia relaxes your muscles and puts you into a deep sleep.
Surgery may be done in 2 ways:
- Laparoscopic surgery is done through several small cuts in the belly. A laparoscope is a lighted tube with a camera. Your provider can put the scope and tools into your belly through the small cuts.
- You may need open surgery (with bigger cuts in the belly) if you have a lot of bleeding into the abdomen or if your fallopian tube has ruptured and needs repair.
You may go home after the surgery or you may need to stay in the hospital for 1 to 2 days, depending on the type of surgery you have and if you lost a lot of blood.
How can I take care of myself?
Follow the full course of treatment prescribed by your healthcare provider. Ask your provider:
- How long it will take to recover
- If there are activities you should avoid and when you can return to your normal activities
- How to take care of yourself at home
- What symptoms or problems you should watch for and what to do if you have them
Make sure you know when you should come back for a checkup.
How can I help prevent an ectopic pregnancy?
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) and sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) can be prevented if you practice safe sex:
- Use latex or polyurethane condoms during foreplay and every time you have vaginal, oral, or anal sex.
- Have just 1 sexual partner who is not having sex with anyone else.
- If you have had sex and are worried that you may have been infected, see your healthcare provider even if you don’t have any symptoms.