Endometrial Biopsy
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
- An endometrial biopsy is a procedure for taking a sample of the lining of the uterus for testing.
- This procedure may be done to diagnose the cause of vaginal bleeding, or to help find out why you are having trouble getting pregnant. This procedure may also be done to check how well treatment for a problem is working.
- Ask your provider how long it will take to recover and how to take care of yourself at home.
- Make sure you know what symptoms or problems you should watch for and what to do if you have them.
________________________________________________________________________
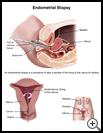
What is an endometrial biopsy?
An endometrial biopsy is a procedure for taking a sample of the lining of the uterus for testing. The uterus is the organ at the top of the vagina. Babies develop in the uterus, and menstrual blood comes from the uterus. The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium.
When is it used?
This procedure may help your healthcare provider find the cause of medical problems you may be having, such as:
- Your uterus is bleeding too much, at the wrong times, or not at all
- You are having bleeding after menopause
- You are having trouble getting pregnant
This procedure may also be done to check how well treatment for a problem is working.
How do I prepare for this procedure?
- Tell your healthcare provider if you think you may be pregnant. Your provider may wait to do this procedure until after your baby is born.
- Your healthcare provider may recommend that you do not douche, use vaginal creams or ointments, or have sex for a few days before the exam.
- You may or may not need to take your regular medicines the day of the procedure. Tell your healthcare provider about all medicines and supplements that you take. Some products may increase your risk of side effects or bleeding. Ask your healthcare provider if you need to avoid taking any medicine or supplements before the procedure.
- Tell your healthcare provider if you have any food, medicine, or other allergies such as latex.
- Follow any other instructions your provider may give you.
- Ask any questions you have before the procedure. You should understand what the healthcare provider is going to do and how long it will take you to recover.
What happens during the procedure?
You don’t need numbing medicine for this test. The procedure can be done in your healthcare provider's office.
You will lie on your back on the exam table with your knees bent and the heels of your feet in stirrup heel holders. You will be asked to slide your hips to the end of the table and let your knees tilt to each side so that your legs are spread apart.
Then your healthcare provider will gently put a thin, lubricated tool called a speculum into your vagina. The speculum holds open the walls of the vagina so your provider can see the cervix (the opening of the uterus). Your provider will insert a tiny straw-like tube into your vagina and then into the uterus through the cervix. The tube will be used to remove a sample of the lining of the uterine wall. The sample will go to the lab for tests.
You may have mild cramps during the procedure.
What happens after the procedure?
You may go home after the procedure. You may have some cramping and bleeding for a few days after the procedure.
Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions. Ask your provider:
- How and when you will get your test results
- If there are activities you should avoid and when you can return to your normal activities
- How to take care of yourself at home
- What symptoms or problems you should watch for and what to do if you have them
Make sure you know when you should come back for a checkup. Keep all appointments for provider visits or tests.
What are the risks of this procedure?
Every procedure or treatment has risks. Some possible risks of this procedure include:
- The uterus may be injured or punctured by the tool used to get a sample.
- You may have infection or bleeding.
Ask your healthcare provider how the risks apply to you. Be sure to discuss any other questions or concerns that you may have.