Gout
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
- Gout is pain, redness, and swelling in a joint, or kidney problems, caused by uric acid crystals.
- Your provider will recommend that you avoid drinking alcohol and eating certain foods to prevent problems. You may also be treated with medicine.
- It helps if you avoid foods such as large amounts of beef, chicken, pork, liver, anchovies, sardines, mussels, and beans. Also, don’t drink large amounts of alcohol.
________________________________________________________________________
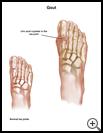
What is gout?
Gout is a condition caused by having too much uric acid in your body. Uric acid is a waste product your body makes when it breaks down certain chemicals called purines. Purines are in many foods, but are especially high in organ meats, dried beans and peas and anchovies. Normally, uric acid dissolves in the blood and passes through your kidneys and out of the body in your urine. If the level of uric acid builds up in the blood, sharp uric acid crystals may form in your joints or under your skin. The crystals cause pain and swelling. If not treated, the uric acid crystals can cause kidney stones and kidney damage.
Usually the uric acid levels have to be high for many years before you start having gout. Uric acid levels in men start to go up after puberty. Women's uric acid levels usually do not go up until after menopause. Gout can start at any age, but is most common in middle-aged men.
What is the cause?
Gout usually happens because too much uric acid is in your blood. This may be because:
- Your kidneys do not get rid of enough uric acid. The reason this happens is not always known. You may be at higher risk for gout if you have a disease such as high blood pressure, diabetes, kidney disease, or a problem with your red blood cells.
- Your body makes too much uric acid. This is more likely if:
- You eat a lot of seafood and meat, especially game such as deer (venison), and organ meats, like liver.
- You drink a lot of alcohol, particularly beer, which increases your uric acid levels.
- You have a family history of too much uric acid in the blood.
- You take medicines that raise the level of uric acid in the blood.
Gout is similar to a condition called pseudogout. Pseudogout also causes joint pain and swelling, but is caused by a buildup of calcium crystals instead of uric acid. The treatment of pseudogout is different from gout.
What are the symptoms?
Many people have high uric acid blood levels for years and never have any symptoms. Sudden attacks sometimes happen with illness, injury, or drinking too much alcohol. The symptoms may last for days to weeks. Gout symptoms may include:
- Sudden, severe pain, often in just 1 joint at a time
- Redness and swelling of a joint
Usually gout first affects your big toe. Later attacks may affect other joints.
If uric acid crystals cause kidney stones, symptoms may include:
- Severe, crampy pain in your back, side, or belly
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- Blood in the urine
How is it diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms and your medical history and examine you.
Tests may include:
- Blood tests
- Joint aspiration, which uses a needle to take fluid from a joint. Removing fluid can also help relieve some of the pain and swelling of gout.
- X-rays
How is it treated?
Usually, if you have high uric acid levels but no symptoms, you will not need treatment. If you have a family history of gout or kidney stones, you may be treated for gout even though you do not have any symptoms. Discuss this with your healthcare provider.
If you have symptoms of gout, you may be prescribed medicine to:
- Stop pain and inflammation
- Lower uric acid levels
Aspirin is not usually recommended because it may keep your kidneys from getting rid of the uric acid.
Your provider will recommend that you avoid drinking alcohol and eating certain foods to prevent problems.
You may start feeling better 1 to 2 days after you start treatment. If gout is not treated, it could last a few days to several weeks. Gout can also come back after months or years.
How can I take care of myself?
Follow the full course of treatment prescribed by your healthcare provider. Make the changes in your diet, the liquids you drink, and alcohol use as recommended by your healthcare provider. Take all medicines as directed. Ask your provider:
- How and when you will get your test results
- How long it will take to recover
- If there are activities you should avoid and when you can return to your normal activities
- How to take care of yourself at home
- What symptoms or problems you should watch for and what to do if you have them
Make sure you know when you should come back for a checkup. Keep all appointments for provider visits or tests.
A healthy lifestyle may also help:
- If you smoke, try to quit. Talk to your healthcare provider about ways to quit smoking.
- If you want to drink alcohol, ask your healthcare provider how much is safe for you to drink.
- Stay fit with the right kind of exercise for you. Talk with your healthcare provider before you start an exercise program.
- Try to get at least 7 to 9 hours of sleep each night.
- Try to keep a healthy weight. If you are overweight, lose weight. Losing some weight can reduce the stress on your joints.
- Use a warm washcloth or heating pad set on the lowest setting to help lessen pain. You can put heat on the painful joint for 15 to 30 minutes 3 to 4 times a day. Be careful not to fall asleep with a heating pad on. It could cause a burn.
- Contact your healthcare provider if you have new or worsening symptoms.
How can I help prevent gout?
There is no sure way to prevent gout. However, you can take these steps to lessen the chance that you will have high uric acid levels:
- Avoid foods such as:
- Organ meats, such as liver and kidney
- Large amounts of beef, chicken, or pork
- Anchovies, sardines, and mussels
- Beans
- Don’t drink large amounts of alcohol, especially beer. Alcohol increases uric acid in your body, and can make gout medicine less effective.