The Human Heart
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
- The human heart is a muscle about the size of your fist. Your heart has 4 chambers and 4 valves that keep blood flowing in the right directions through the heart.
- An electrical signal in your heart starts each heartbeat, causing the heart muscle to squeeze and pump blood. The usual rate of heartbeats when you are resting is between 60 and 100 beats per minute.
________________________________________________________________________
The human heart is a muscle about the size of your fist. It pumps your blood through your body. It starts pumping during the 4th week of a baby’s development. This pumping is heard as your heartbeat. Your heart beats about 35 million times a year throughout your life. The only rest period for your heart muscle is the short time between heartbeats. Death happens when your heart stops beating.
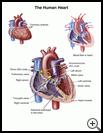
What are the parts of the heart?
The heart has 4 sections, or chambers. The upper chambers are each called atria, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. Your heart muscle squeezes to push blood through these 4 chambers, to your lungs, and to the rest of your body. Blood flows from the right atrium into the right ventricle, and the right ventricle pumps it to the lungs.
As it passes through the lungs, the blood picks up oxygen and leaves behind carbon dioxide. Then the blood flows back to the heart and into the left atrium, and from there into the left ventricle. The left ventricle pumps the blood out to the rest of the body, with a small amount going to the heart muscle itself. Your heart pushes blood out through your arteries and blood returns to your heart through your veins.
What are heart valves?
Your heart has 4 valves that open and close with each heartbeat to keep the blood flowing in the right direction through the heart.
- The tricuspid valve helps blood flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle.
- The pulmonary valve helps blood flow from the right ventricle to the lungs.
- The mitral valve helps blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle.
- The aortic valve helps blood flow from the left ventricle into the big blood vessel (aorta) that carries blood to the rest of your body.
The 4 heart valves work with the chambers in a pattern to keep blood flowing in 1 direction. They are made of thin tissues that open and close easily. The valves are closed while the chambers fill with blood and then they open to push blood out.
What causes the heart to beat?
An electrical signal in your heart starts each heartbeat, causing the heart muscle to squeeze (pump). Normally, this signal starts in the upper right chamber of the heart (the right atrium). The signal then follows a normal path to the left atrium and to the lower chambers of the heart (the ventricles).
The usual rate of heartbeats when you are resting is between 60 and 100 beats per minute. Your heart may beat faster or slower than normal because of:
- Infections
- Emotions, like anxiety, stress, excitement, or anger
- Medicines, supplements, or caffeine
- Exercise
- Pain
- Thyroid problems
- Some heart problems
- Anemia (a low level of red blood cells)
The heart is much more sensitive to oxygen than other muscles in your body. Your heart can be damaged quickly if it doesn't get enough oxygen from the blood.