Knee Sprain
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
- A knee sprain is stretching or tearing of one or more ligaments in your knee that connects one bone to another.
- Change or stop doing the activities that cause pain until the sprain heals.
- A knee sprain can be treated with bandages or braces, ice, exercise, and sometimes medicine. Usually, surgery is not needed.
________________________________________________________________________
What is a knee sprain?
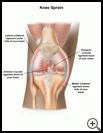
A knee sprain is an injury to one or more ligaments in your knee. Ligaments are strong bands of tissue that connect one bone to another to form the joints. The ligaments in your knee keep your knee and leg bones in place when you walk or run. When a ligament is injured, it can be stretched, partially torn, or completely torn. Complete tears make the knee joint very loose and unstable.
The main ligaments in your knee are the medial collateral ligament, the lateral collateral ligament, the anterior cruciate ligament, and the posterior cruciate ligament.
What is the cause?
A knee sprain is caused by a sudden activity that twists or tears a ligament. It can happen, for example, when you play sports, when you fall, or if you are in an accident that twists your leg.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms may include:
- A loud, painful pop at the time of the injury
- Swelling of your knee
- Trouble bending or straightening your knee
- Pain around your knee
- A feeling like your knee is loose or unstable
How is it diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, activities, and medical history and examine you. You may have X-rays or other scans.
How is it treated?
You will need to change or stop doing the activities that cause pain until the ligament has healed.
Your provider may recommend stretching and strengthening exercises to help you heal.
Your provider may wrap an elastic bandage around your knee to keep swelling from getting worse. You may need to keep your knee in a knee immobilizer and use crutches to protect your knee while you heal.
Usually surgery is not needed unless you have a complete ligament tear or several ligaments are hurt at the same time.
The pain often gets better within a few weeks with self-care, but some injuries may take several months or longer to heal. It’s important to follow all of your healthcare provider’s instructions.
How can I take care of myself?
To keep swelling down and help relieve pain for the first few days after the injury:
- Put an ice pack, gel pack, or package of frozen vegetables wrapped in a cloth on the injured area every 3 to 4 hours for up to 20 minutes at a time.
- Keep your knee up on pillows so that it is above the level of your heart when you sit or lie down.
- Take nonprescription pain medicine, such as acetaminophen, ibuprofen, or naproxen. Read the label and take as directed. Unless recommended by your healthcare provider, you should not take these medicines for more than 10 days.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin, may cause stomach bleeding and other problems. These risks increase with age. Putting an NSAID gel on your skin can decrease pain, with fewer side effects than pills taken by mouth. Ask your healthcare provider if a prescription is right for you.
- Acetaminophen may cause liver damage or other problems. Unless recommended by your provider, don't take more than 3000 milligrams (mg) in 24 hours. To make sure you don’t take too much, check other medicines you take to see if they also contain acetaminophen. Ask your provider if you need to avoid drinking alcohol while taking this medicine.
Follow your healthcare provider's instructions, including any exercises recommended by your provider. Ask your provider:
- How and when you will get your test results
- How long it will take to recover
- If there are activities you should avoid and when you can return to your normal activities
- How to take care of yourself at home
- What symptoms or problems you should watch for and what to do if you have them
Make sure you know when you should come back for a checkup. Keep all appointments for provider visits or tests.
How can I help prevent a knee sprain?
Warm-up exercises and stretching before activities can help prevent injuries. For example, do exercises that build strong thigh and hamstring muscles and stretch your leg muscles.
Follow safety rules and use any protective equipment recommended for your work or sport. For example, if you ski, make sure your ski bindings are set correctly by a trained professional so that your skis will release if you fall.