Bile Duct PTHC Exam
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
- A PTHC exam that uses X-rays and dye put through a needle inserted through your liver to check your liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts.
- PTHC can find problems such as gallstones, cancer, scar tissue, or other problems. If a buildup of bile or a blockage is found, your provider may insert a catheter or a stent to drain fluid out of the bile duct. This helps prevent infections or other illness.
- Ask your healthcare provider how and when you will hear your test results.
- Make sure you know what symptoms or problems you should watch for and what to do if you have them.
________________________________________________________________________
What is a bile duct PTHC exam?
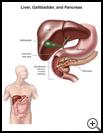
A percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram (PTHC) is an exam that uses X-rays and contrast dye put through a needle inserted through your liver to check your liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts.
The liver and gallbladder are part of your digestive system. Your liver makes bile, which helps your body break down the fat in food. Ducts in the liver carry bile to the gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small sac under your liver on your right side that stores bile. The bile duct carries bile from the gallbladder to the small intestines.
When is it done?
PTHC can find problems such as gallstones, cancer, scar tissue, or other problems. A PTHC is often done when another procedure, called an ERCP can’t be done or has failed. An ERCP is an exam done with a thin, flexible tube with a camera on the end that is passed through your throat and into your small intestines.
How do I prepare for this procedure?
- Plan for your care and find someone to give you a ride home after the procedure.
- Your healthcare provider will tell you when to stop eating and drinking before the procedure. This helps to keep you from vomiting during the procedure.
- You may or may not need to take your regular medicines the day of the procedure. Tell your healthcare provider about all medicines and supplements that you take. Some products may increase your risk of side effects. Ask your healthcare provider if you need to avoid taking any medicine or supplements before the procedure.
- Tell your healthcare provider if you have any food, medicine, or other allergies such as latex.
- Follow your healthcare provider's instructions about not smoking before and after the procedure. Smokers may have more breathing problems during the procedure and heal more slowly. It is best to quit 6 to 8 weeks before surgery.
- Follow any other instructions your healthcare provider gives you.
- Ask any questions you have before the procedure. You should understand what your healthcare provider is going to do. You have the right to make decisions about your healthcare and to give permission for tests or procedures.
What happens during this procedure?
The test may be done at an outpatient clinic. It usually takes 30 minutes to 1 hour.
Before the procedure, you will be given medicine to help you relax, but you may be awake during the procedure. You will be given a local anesthetic to numb the area. You will lie on your back on a table that tilts. A long, thin, flexible needle will be inserted through your skin high on the right side of your belly into your liver. Contrast dye will be injected and your healthcare provider will watch the contrast dye moving through the bile ducts on a computer screen. X-rays will also be taken.
If a buildup of bile or a blockage is found, your provider may insert either a thin flexible tube, called a catheter, or a stiff tube, called a stent, through the blockage. This will allow fluid to drain out of the bile duct, either into a bag attached to your side or into your small intestine. It will also prevent bile from building up in your blood or liver. Removing the bile allows your provider to get better X-rays of your bile duct and helps prevent infections or other illness.
If a blockage is found during the test, you may need another procedure or surgery to remove the blockage.
What happens after this procedure?
After the test, you will need to rest in bed for 3 to 6 hours or more.
Ask your healthcare provider:
- How and when you will get your test results
- How long it will take to recover
- If there are activities you should avoid, including how much weight you can lift and when you can return to your normal activities
- How to take care of yourself at home, especially if you have a bile drainage bag placed
- What symptoms or problems you should watch for and what to do if you have them
Make sure you know when you should come back for a checkup. Keep all appointments for provider visits or tests.
What are the risks of PTHC?
Every procedure or treatment has risks. Some possible risks of this procedure include:
- You may have problems with anesthesia.
- In rare cases, you may have an allergic reaction to medicines used during the procedure.
- You may have infection, bleeding, or blood clots.
- You may have a collapsed lung.
Ask your healthcare provider how these risks apply to you. Be sure to discuss any other questions or concerns that you may have.