Retinal Detachment
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
- Retinal detachment means that the lining at the back of your eye pulls away from the tissue under it. It can cause blindness if not treated right away.
- Depending on the cause, treatment may include medicine, or most commonly, surgery.
- See your eye care provider regularly so that any problems can be corrected before they become serious.
________________________________________________________________________
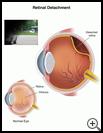
What is retinal detachment?
The retina is the lining at the back of the eye that senses light coming into your eye. A retinal detachment is when the retina pulls away from the tissues under it. A retinal detachment is very serious and needs to be treated promptly to save your vision.
What is the cause?
A retinal detachment is usually caused by one of two problems:
- The clear gel that fills the center of the eye can turn into liquid and pull on your retina. This can cause holes or tears. If fluid gets through the tear and behind the retina, the retina can separate from the back wall of your eye.
- Scar tissue can form on the surface of the retina, pulling it away from the back of your eye. Most often, scar tissue grows in response to injury, eye surgery, or diseases such as diabetes or sickle cell disease.
Other problems that may increase your risk of retinal detachment include:
- Nearsightedness
- A growth in your eye or an eye infection
- Having had a retinal detachment in your other eye
- Other people in your family who have had retinal problems
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms of a retinal detachment include:
- An increase in floaters, which are dark spots or squiggles in your vision
- Flashes, which are flickers or arcs of light in your side vision
- A gradual loss of side vision, which is like a curtain slowly being pulled across the front of your eye
Call your provider or go to the emergency room right away if you have these symptoms. If not treated, you may have a complete loss of vision within hours or months.
How is it diagnosed?
Your eye care provider will ask about your symptoms and medical history and do exams and tests such as:
- An exam using a microscope with a light attached, called a slit lamp, to look closely at the front and back of your eye
- An exam using drops to enlarge, or dilate, your pupils and a light to look into the back of your eyes
- An ultrasound, which uses sound waves to show pictures of the back of your eye
How is it treated?
If retinal detachment is caused by swelling or infection, treating those problems may be all that is needed. Other types of retinal detachment are usually treated with surgery. Different types of surgery include putting a band around the eye or placing gas or oil in the eye to reattach the retina. For most of the procedures, you can go home the same day. Your vision may be very blurry after surgery. It may take several weeks or months for the blurriness to go away. If the detachment is severe, your vision may never get back to normal.
While you recover, you may need to keep your head in a certain position, such as facing the floor, for several days or weeks so your retina heals in the right position. Your provider will tell you what position to rest your head in, how long you need to do this each day, and for how many days or weeks. Special furniture is available that can help you keep your head positioned comfortably during your recovery. Ask your provider for more information about this.
How can I take care of myself?
Follow the full course of treatment your healthcare provider prescribes. Ask your healthcare provider:
- How and when you will get your test results
- How long it will take to recover
- If there are activities you should avoid and when you can return to your normal activities
- How to take care of yourself at home
- What symptoms or problems you should watch for and what to do if you have them
Make sure you know when you should come back for a checkup, and when you need to be checked for a change in eyeglasses prescription.
Sometimes scar tissue can form even after a retinal detachment is fixed. You may surgery to remove the scar. If your vision gets worse or you start having new vision problems after surgery, let your provider know.
How can I help prevent retinal detachment?
If you are very nearsighted or have a family history of retinal detachments, see your eye care provider regularly. While you cannot prevent some changes in your eyes, finding and treating holes and tears promptly helps prevent retinal detachment.
If you have had retinal detachment in one eye, your risk of retinal detachment in the other eye is greater. See your eye care provider regularly so that any problems in your other eye can be corrected before they become more serious.