Dilation and Curettage (D&C)
________________________________________________________________________
KEY POINTS
- Dilation and curettage (D&C) is a procedure used to remove tissue from the uterus by opening the cervix and scraping the uterus.
- You will be given a regional or general anesthesia to keep you from feeling pain during the procedure.
- Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for taking care of yourself at home. Your provider will tell you what symptoms or problems you should watch for and what to do if you have them.
________________________________________________________________________
What is a dilation and curettage?
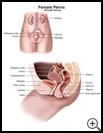
Dilation and curettage (D&C) is a procedure used to remove tissue from the uterus. The uterus is the muscular organ at the top of the vagina. Babies grow in the uterus, and menstrual blood comes from the uterus.
Dilation opens and widens the opening of the uterus (cervix). Curettage means that a sharp tool is used to scrape the walls of the uterus and remove tissue from inside the uterus.
When is it used?
D&C may be done to:
- Find the cause of abnormal bleeding from the uterus
- Treat abnormal bleeding from the uterus
- Remove polyps from the uterus
- Remove an IUD (a birth control device) that is out of place in the uterus
- Remove tissue remaining after a miscarriage or childbirth
- Terminate a pregnancy (also called an abortion)
Ask your healthcare provider about your choices for treatment and the risks.
How do I prepare for a D&C?
- Make plans for your care and recovery after you have the procedure. Find someone to give you a ride home after the procedure. Allow for time to rest and try to find other people to help with your day-to-day tasks while you recover.
- Follow your provider's instructions about not smoking before and after the procedure. Smokers may have more breathing problems during the procedure and heal more slowly. It is best to quit 6 to 8 weeks before surgery.
- You may or may not need to take your regular medicines the day of the procedure. Tell your healthcare provider about all medicines and supplements that you take. Some products may increase your risk of side effects. Ask your healthcare provider if you need to avoid taking any medicine or supplements before the procedure.
- Tell your healthcare provider if you have any food, medicine, or other allergies such as latex.
- Your provider will tell you when to stop eating and drinking before the procedure. This helps to keep you from vomiting during the procedure.
- Follow any other instructions your healthcare provider gives you.
- Ask any questions you have before the procedure. You should understand what your healthcare provider is going to do and how long it will take to recover. You have the right to make decisions about your healthcare and to give permission for any tests or procedures.
What happens during the procedure?
The procedure is usually done in a surgery center, clinic, or hospital.
You will be given a regional or general anesthesia to keep you from feeling pain during the procedure. Regional anesthesia numbs part of your body while you stay awake. If you have regional anesthesia, you may also be given medicine to help you relax. The medicine can make you drowsy or you may fall asleep before the procedure. General anesthesia relaxes your muscles and you will be asleep.
Your healthcare provider gently stretches open your cervix and guides a thin tool called a curette into the uterus. Your provider uses the tool to scrape the lining of the uterus and remove tissue. Sometimes a suction tube is used in addition to the curette. The tissue is usually sent to the lab for tests.
What happens after the procedure?
After the procedure, you may stay in a recovery area for a few hours. Expect some bleeding and menstrual-type cramps for the first day or so. Your healthcare provider may suggest a pain medicine to relieve the discomfort.
Women who are still having periods may have their next period a little earlier or later than normal. This is because it takes time for the lining in your uterus to build up again after the D&C. Until your cervix closes, bacteria from the vagina can enter the uterus and cause infection. Do not put anything into your vagina after the procedure. Ask your healthcare provider when you can have sex or use tampons again.
Follow your provider's instructions. Ask your provider:
- How and when you will get your test results
- How long it will take to recover
- If there are activities you should avoid and when you can return to your normal activities
- How to take care of yourself at home
- What symptoms or problems you should watch for and what to do if you have them
Make sure you know when you should come back for a checkup. Keep all appointments for provider visits or tests.
What are the risks of this procedure?
Every procedure or treatment has risks. Some possible risks of this procedure include:
- You may have problems with anesthesia.
- You may have infection or bleeding.
- The uterus may be punctured or scar tissue may form inside the uterus. You might then need more surgery.
Ask your healthcare provider how these risks apply to you. Be sure to discuss any other questions or concerns that you may have.